A practical step-by-step on how to transcribe and translate DNA sequence
DNA
transcription and translation are common terms in DNA replication. Therefore,
for one to understand and master how to transcribe and translate a particular
DNA sequence, one needs to know the meaning of DNA replication, DNA
transcription, and DNA translation. DNA replication is defined as the synthesis
of daughter DNA from the parental DNA. DNA transcription is the process of
synthesizing RNA using the DNA template. DNA translation is the process of
synthesizing proteins using the messenger RNA (mRNA) as the template. Additionally,
one has to comprehend the roles of transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA)
in DNA transcription and translation. mRNA transfers the genetic information
from the DNA to the ribosomes, where they identify the sequence of the protein
product. On the other hand, tRNA interprets the genetic information carried by the
messenger RNA into protein. tRNA acts as the physical link between the protein
amino acid sequence and the messenger RNA. tRNA has anticodon and covalent
attachment ends. The anticodon creates three base pairs with the mRNA codon
while the covalent attachment end attaches to the amino acid that resembles the
anticodon sequence.
After
knowing the basis of DNA replication, the next step is to determine how a given
DNA sequence can be transcribed and translated.
First
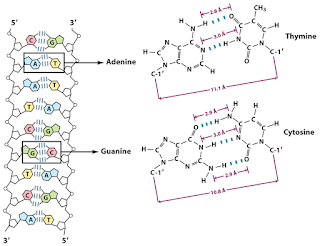
one has to know the Chargaff''s base pairing rule. According to this rule; in DNA,
Adenine(A) pairs with thymine (T) in double bonds while cytosine pairs
with the guanine in triple bonds. In RNA, thymine is replaced with the
uracil(U). Picture 1 shows how
these bonds occur in DNA structure.
 |
| Picture 1 |
Step 1: DNA transcription
Take
the strand of the provided DNA sequence and transcribe into the messenger RNA
by replacing A with U, T with A, G with C and C with G. The resulting mRNA
should be complimentary to the DNA.
Step 2: DNA translation
tRNA
reads the genetic information in mRNA in form of codon. 1 codon equals to three
base pairs which give one amino acid corresponding to the continuous codon
sequence of mRNA. Codon of specific
amino acid is provided in the genetic code table as shown in Picture 2.
 |
| Picture 2 |
Example:
Transcribe
and translate the following sequence of DNA: TTAACGCCA. There is a mutation
that resulted in AAA being inserted after G. Predict how this mutation would
impact the product of translation.
Solutions:
In
this problem, we replace T with A, A with U, C with G and G with C to get the
following mRNA sequence.
AAUUGCGGU
This
mRNA sequence gives three codons(AAU, UGC, and GGU). These codons are then
checked on the genetic code table to determine which amino acids they
represent. The answers to this question are provided in Picture 3.
 |
| Picture 3 |
Mutation
introduces additional amino acid (phenylalanine) in the normal sequence of polypeptide of synthesized protein.
By
following these steps, you can easily transcribe, and translate any DNA
sequence. If there is anything you feel is tackled well you can share in the
comment.



👍👍
ReplyDelete